Poker Hands
At PokerStars, we deal many varieties of poker, some of which use different hand rankings. Hold’em, Omaha, Seven Card Stud and Five Card Draw all use the traditional ‘high’ poker rankings. Omaha Hi/Lo, Razz and Stud Hi/Lo use the ‘Ace to Five’ (‘California’) low hand rankings for low hands. 2-7 Single Draw and 2-7 Triple Draw use the ‘Deuce to Seven’ (‘Kansas City’) lowball rankings for low hands.
Lastly, Badugi uses a special ranking of hands unique to that game.
Poker Hands – from Best to Worst
Traditional High Poker Hand Ranks
Straight Flush: Five cards in numerical order, all of identical suits.
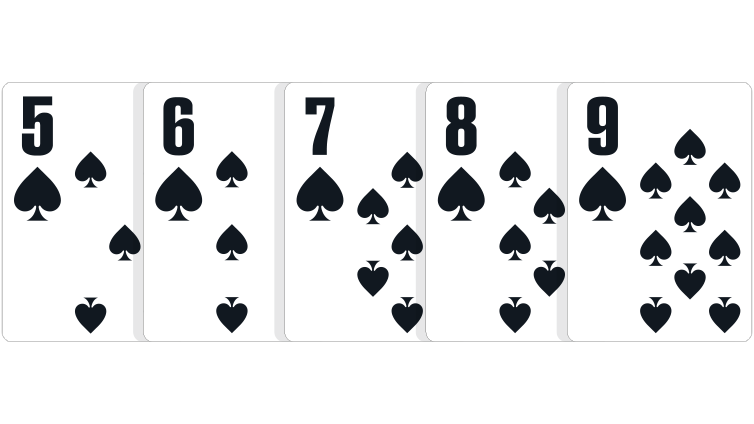
In the event of a tie: Highest rank at the top of the sequence wins.
The best possible straight flush is known as a royal flush, which consists of the ace, king, queen, jack and ten of a suit. A royal flush is an unbeatable hand.
Four of a Kind: Four cards of the same rank, and one side card or ‘kicker’.
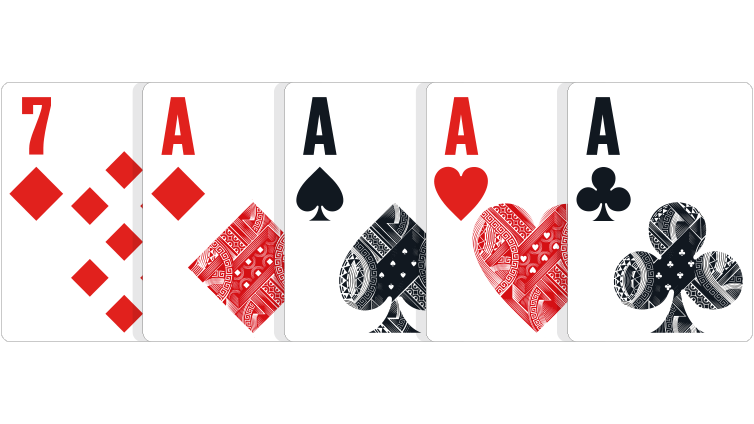

In the event of a tie: Highest four of a kind wins. In community card games where players have the same four of a kind, the highest fifth side card ('kicker') wins.
Full House: Three cards of the same rank, and two cards of a different, matching rank.

In the event of a tie: Highest three matching cards wins the pot. In community card games where players have the same three matching cards, the highest value of the two matching cards wins.
Flush: Five cards of the same suit.
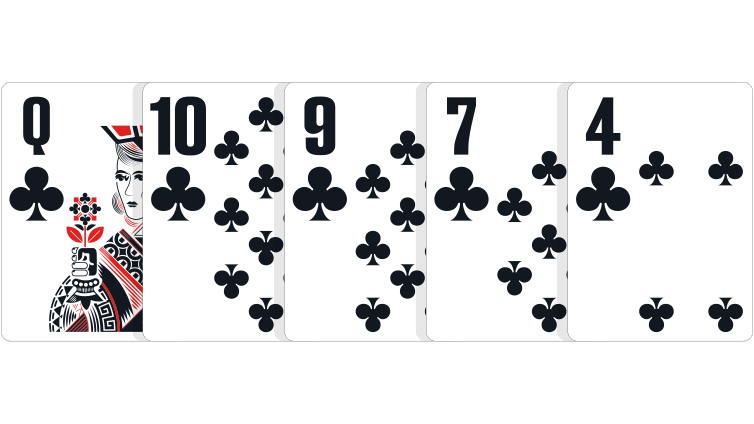
In the event of a tie: The player holding the highest ranked card wins. If necessary, the second-highest, third-highest, fourth-highest, and fifth-highest cards can be used to break the tie. If all five cards are the same ranks, the pot is split. The suit itself is never used to break a tie in poker.
Straight: Five cards in sequence.
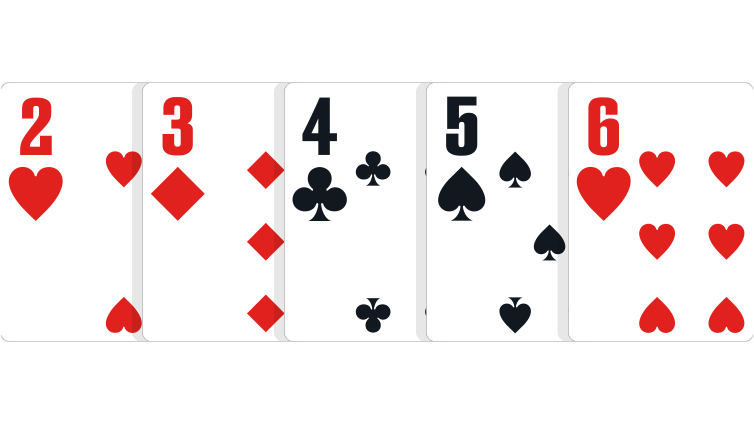

In the event of a tie: Highest ranking card at the top of the sequence wins.
Note: The Ace may be used at the top or bottom of the sequence, and is the only card which can act in this manner. A,K,Q,J,T is the highest (Ace high) straight; 5,4,3,2,A is the lowest (Five high) straight.
Three of a kind: Three cards of the same rank, and two unrelated side cards.
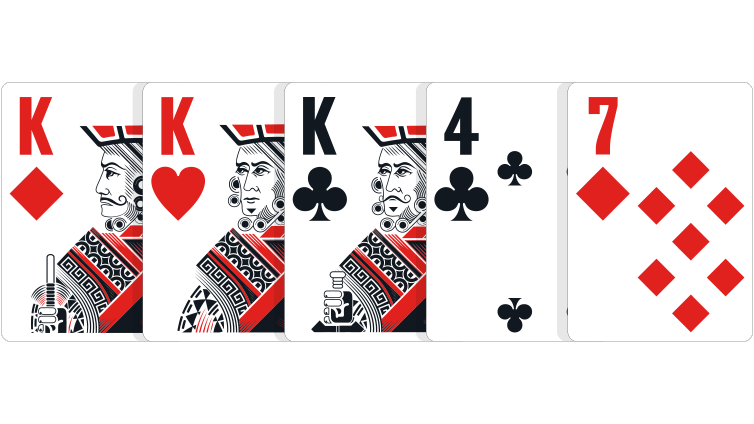

In the event of a tie: Highest ranking three of a kind wins. In community card games where players have the same three of a kind, the highest side card, and if necessary, the second-highest side card wins.
Two pair: Two cards of a matching rank, another two cards of a different matching rank, and one side card.
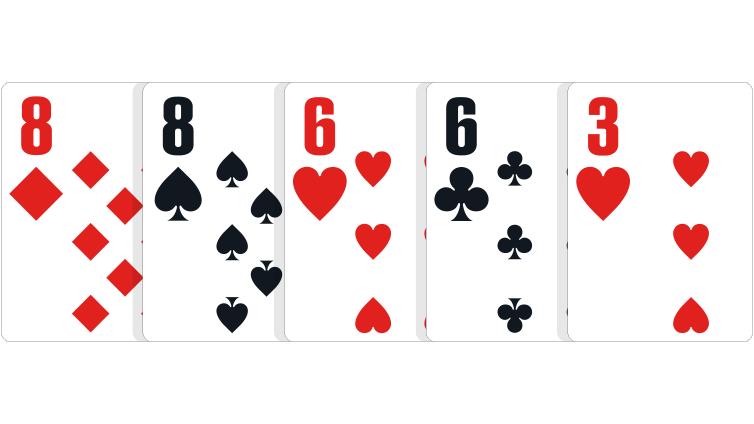

In the event of a tie: Highest pair wins. If players have the same highest pair, highest second pair wins. If both players have two identical pairs, highest side card wins.
One pair: Two cards of a matching rank, and three unrelated side cards.
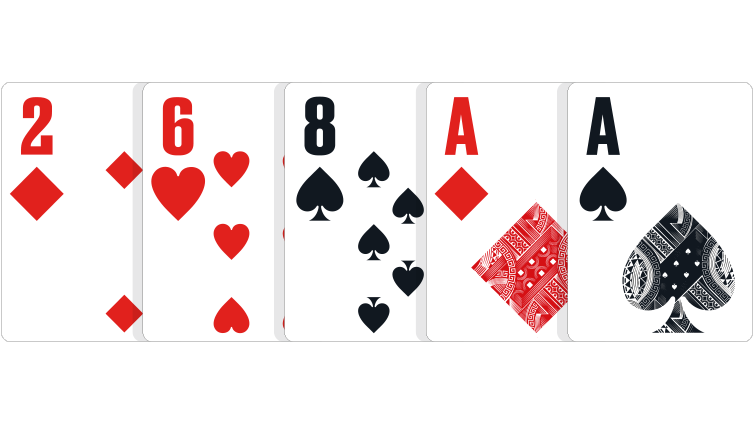

In the event of a tie: Highest pair wins. If players have the same pair, the highest side card wins, and if necessary, the second-highest and third-highest side card can be used to break the tie.
High card: Any hand that does not qualify under a category listed above.
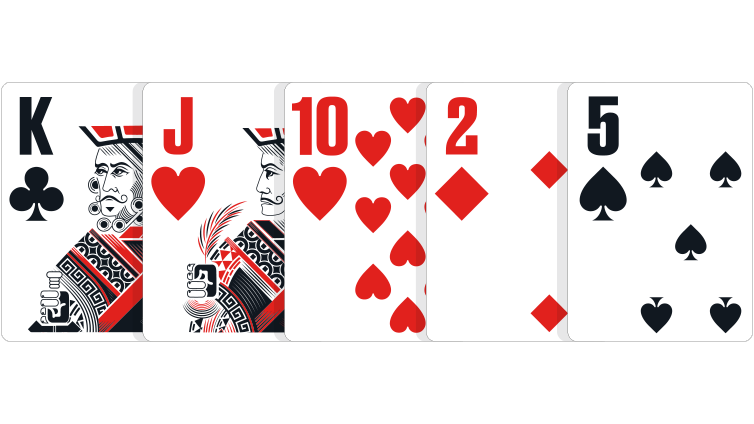

In the event of a tie: Highest card wins, and if necessary, the second-highest, third-highest, fourth-highest and smallest card can be used to break the tie.
Ace To Five Lowball Hand Ranks
This method of ranking low hands is used in traditional Hi/Lo games, like Omaha Hi/Lo and Stud Hi/Lo, as well as in Razz, the ‘low only’ Stud game.
Note that suits are irrelevant for Ace to Five low. A flush or straight does not ‘break’ an Ace to Five low poker hand. Aces are always a ‘low’ card when considering a low hand.
Please also note that the value of a five-card low hand starts with the top card, and goes down from there.
Five Low, or Wheel: The Five, Four, Three, Deuce and Ace.
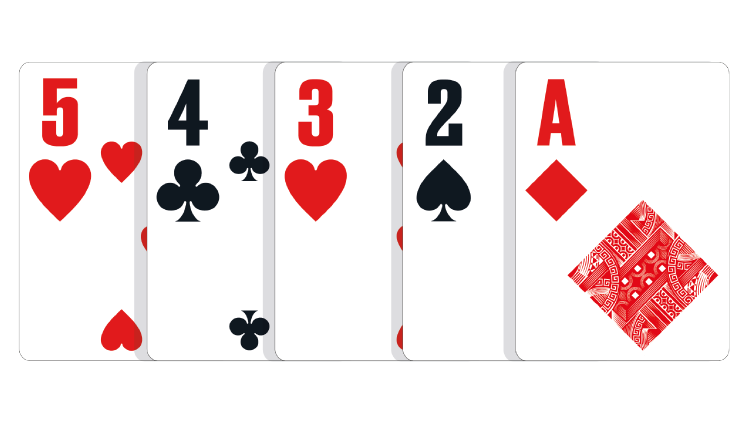

In the event of a tie: All Five-high hands split the pot.
Six Low: Any five unpaired cards with the highest card being a Six.
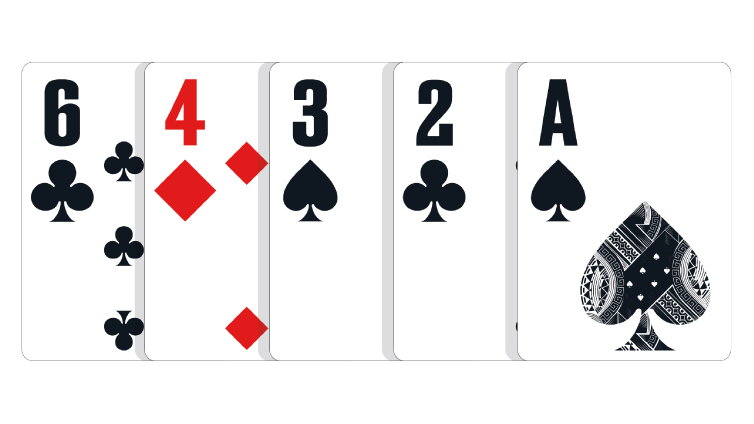

In the event of a tie: The lower second-highest ranking card wins the pot. Thus 6,4,3,2,A defeats 6,5,4,2,A. If necessary, the third-highest, fourth-highest and fifth-highest cards in the hand can be used to break the tie.
Seven Low: Any five unpaired cards with the highest card being a Seven.
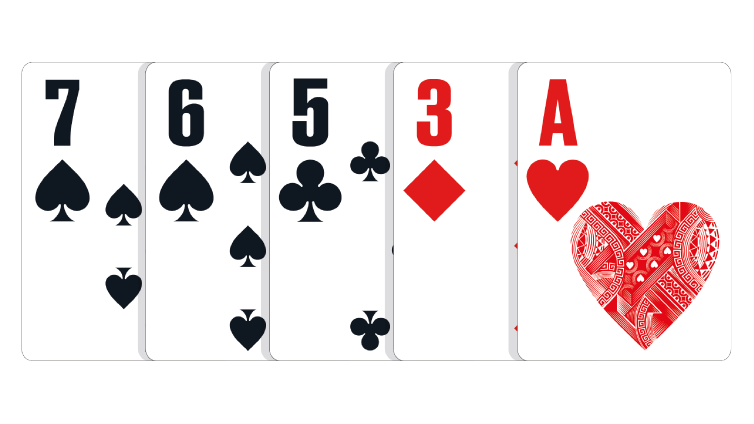

In the event of a tie: The lower second-highest ranking card wins the pot. If necessary, the third-highest, fourth-highest and fifth-highest cards in the hand can be used to break the tie.
Eight Low: Any five unpaired cards with the highest card being an Eight.
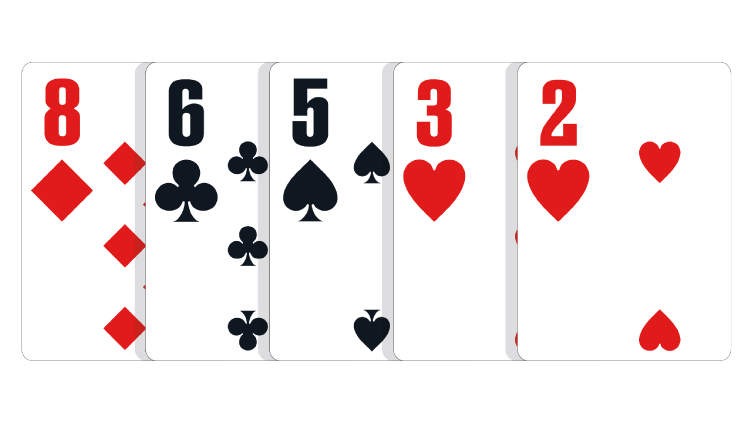

In the event of a tie: The lower second-highest ranking card wins the pot. If necessary, the third-highest, fourth-highest and fifth-highest cards in the hand can be used to break the tie.
An Eight Low is the weakest hand that qualifies for low in Omaha Hi/Lo and Stud Hi/Lo. However in Razz, there is no such ‘qualifier’ and the lowest hand will always win the pot, even if it is a nine low, queen low, or even a pair!
Deuce To Seven Lowball Hand Ranks
The Deuce to Seven Lowball hand rankings are the exact opposite of the traditional ‘high’ hand rankings. Therefore, the worst possible hand in traditional high poker – seven-five high, with different suits, becomes the best possible hand in deuce to seven lowball (a ‘perfect seven’ low or ‘wheel’).
In practice, an ace always plays as a high card in Deuce to Seven (so A,5,4,3,2 is an ace high, not a straight). Straights and flushes count against your hand in Deuce to Seven.
Seven Low: Any five unpaired, unconnected cards of different suits, with the highest card being a seven. The best possible hand is 7,5,4,3,2, also known as a ‘wheel’ or ‘number one’.
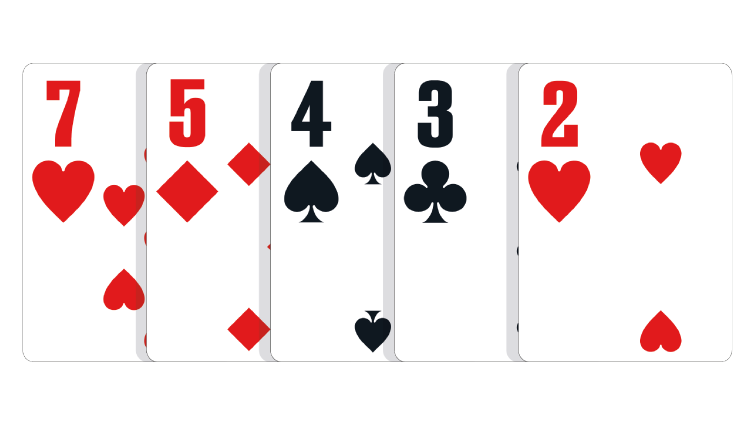

In the event of a tie: The lower second card wins the pot. Thus 7,5,4,3,2 beats 7,6,5,3,2 (a ‘Seven-Five low’ is better than a ‘Seven-Six low’). If necessary, the third-highest, fourth-highest and fifth-highest cards in the hand can be used to break the tie.
Eight Low: Any five unpaired, unconnected cards of different suits, with the highest card being an eight.
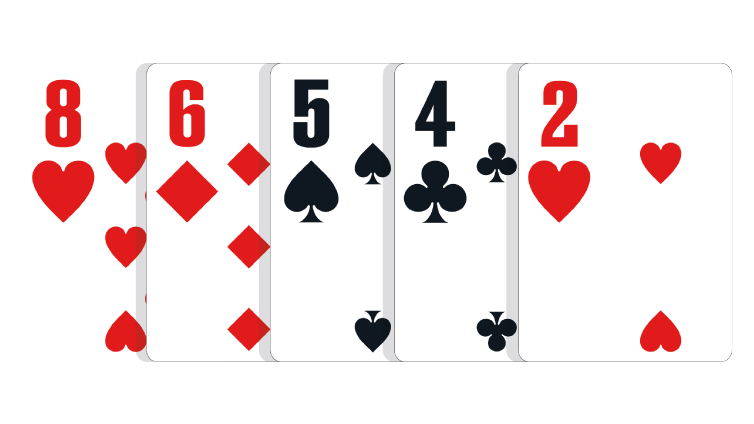

In the event of a tie: The lower second card wins the pot. If necessary, the third-highest, fourth-highest and fifth-highest cards in the hand can be used to break the tie.
Nine Low: Any five unpaired, unconnected cards of different suits, with the highest card being a nine.
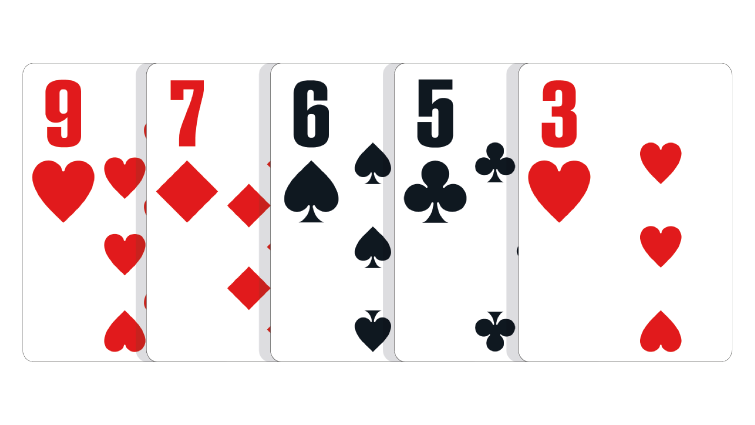

In the event of a tie: The lower second card wins the pot. If necessary, the third-highest, fourth-highest and fifth-highest cards in the hand can be used to break the tie.
Ten Low: Any five unpaired, unconnected cards of different suits, with the highest card being a ten.
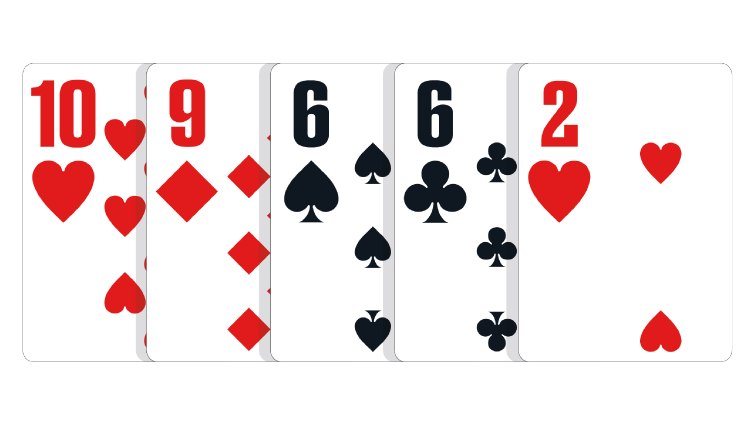

In the event of a tie: The lower second card wins the pot. If necessary, the third-highest, fourth-highest and fifth-highest cards in the hand can be used to break the tie.
Note: There is no ‘qualifier’ for low in Deuce to Seven lowball games. The above are just examples of hands that may come up in play – the lowest hand will always win the pot in Deuce to Seven, even if it is a pair or worse!
Badugi Hand Ranks
Badugi does not use traditional poker hand rankings and it takes some practice to learn how to correctly read the hands. Badugi hand rankings are somewhat related to the Ace to Five rankings; like in Ace to Five, an ace always plays as a low card. However, unlike Ace to Five, each card in your hand must be a different suit and a different rank, in order to count.
Badugi hands consist of four cards, instead of the usual five. Because of this it is impossible to make a five-card straight, and having four cards in sequence does not hurt your hand.
Remember, if you have cards of the same suit, only one of them counts, and if you have pairs, only one of them counts.
Badugi: A badugi is any hand which consists of four unpaired cards, each a different suit.
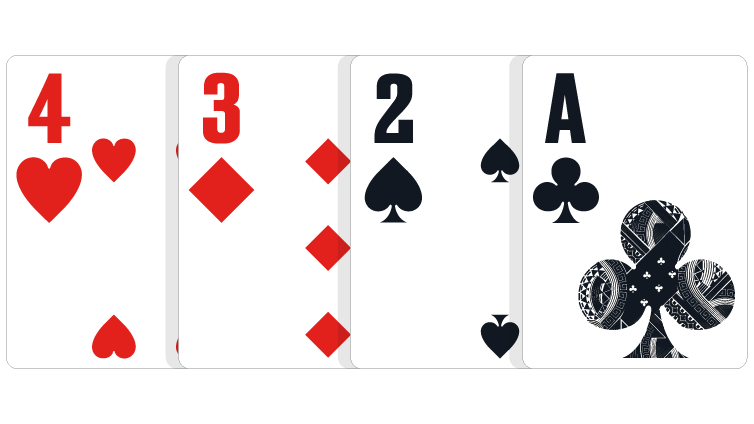

In the event of a tie: The lower second card wins the pot. If necessary, the third-highest and fourth-highest cards in the hand can be used to break the tie.
Three-Card Hand: Any hand consisting of three unpaired cards of different suits, but a fourth paired or suited card. The lowest three unpaired cards of different suits play.
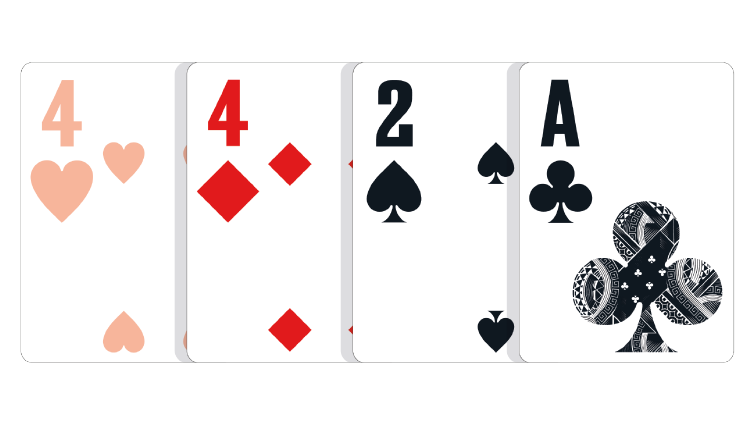

Because there is a pair, one of the fours does not count, so it is simply ignored, making a 4,2,A three-card hand
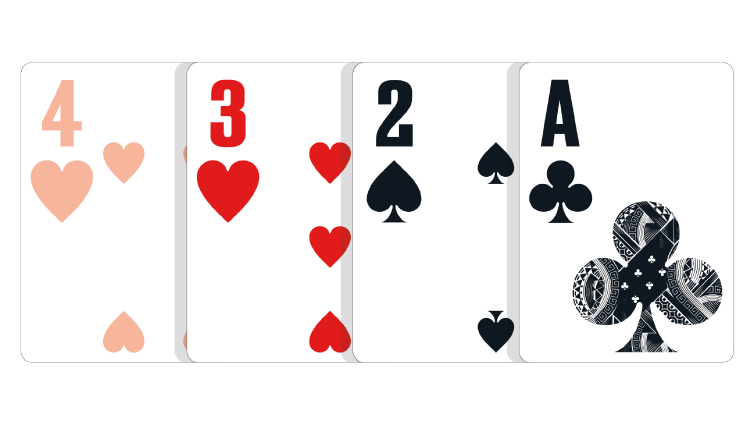

Because there are two hearts in this hand, one of them is ignored, making a 3,2,A three-card hand.
In the event of a tie: The lower second card wins the pot. If necessary, the third-highest card in the hand can be used to break the tie. The fourth (paired or suited) card does not count toward the hand and is not used to break ties.
Two-Card Hand: Any hand consisting of two unpaired cards of different suits, but two paired or suited cards. The lowest two unpaired cards of different suits play.
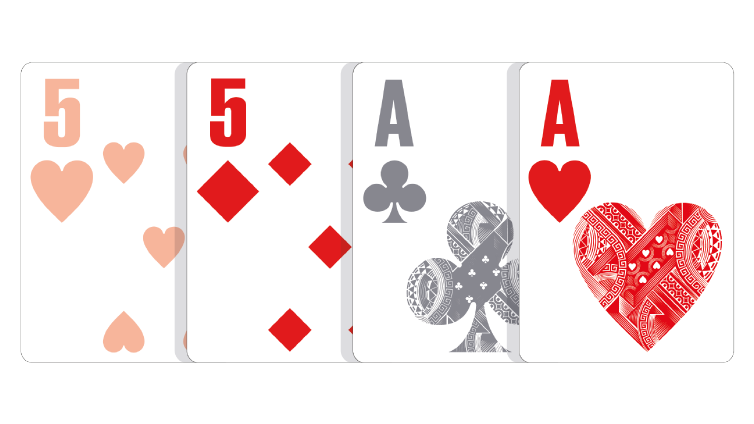

Because there are two pairs, one of each pair is discarded, making a 5,A two-card hand.
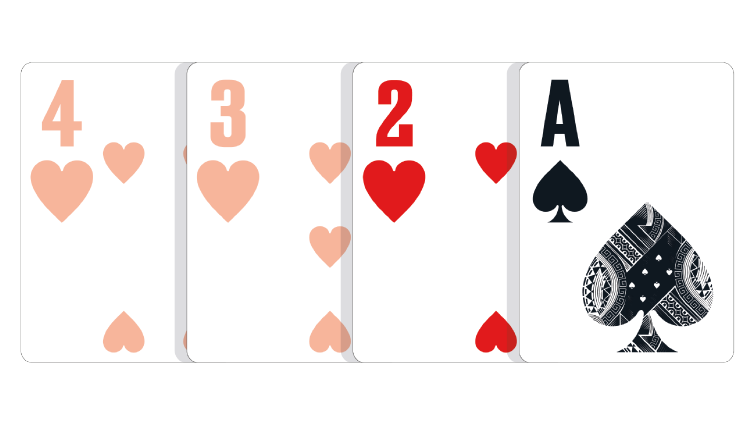
Because there are three hearts, two of them are discarded, making a 2,A two-card hand.
In the event of a tie: The lower second card wins the pot. The third and fourth (paired or suited) cards do not count toward the hand and are not used to break ties.
One-Card Hand: A hand consisting of only one playable card. The lowest card plays.
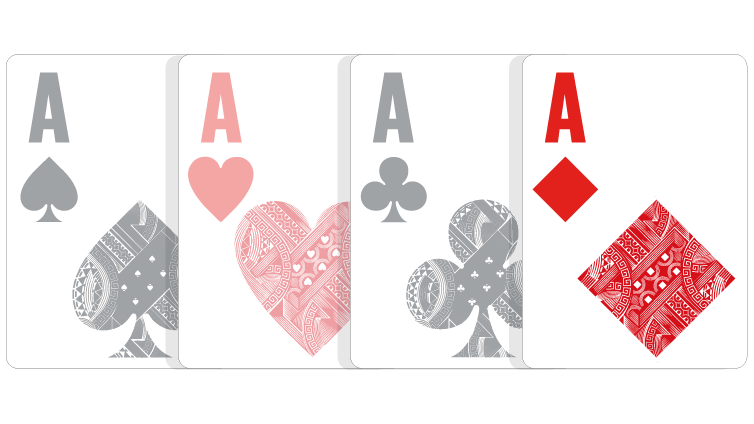

Since there are four Aces, three of them are discarded, making a one-card hand of just an Ace.
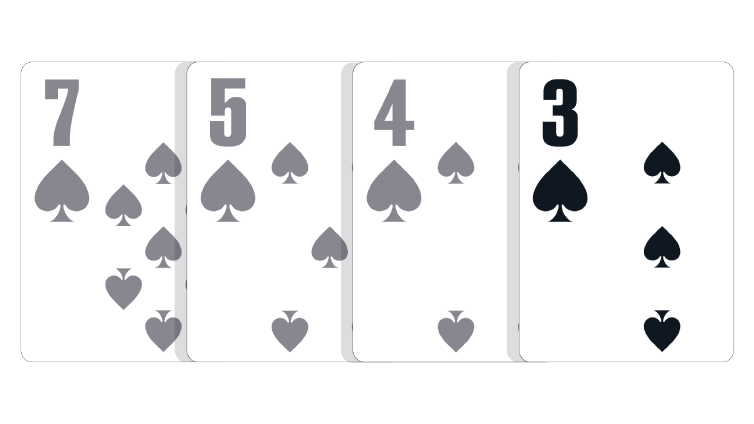
Since there are four cards of the same suit, three of them are discarded, making a one-card hand of just a Three.
In the event of a tie: The pot is split between two equal one-card hands.
How to understand who has the better hand in poker
When you’ve got the hand rankings down, you can then start thinking about the best way to play your hand and how likely it is to beat other hands.
In general, the following rules apply:
- One pair > high card
- Two pair > one pair
- Three of a kind > two pair
- Straight > three-of-a-kind
- Flush > straight
- Full house > flush
- Four of a kind > full house
- Straight flush > four of a kind
- Royal flush > straight flush
How can you calculate poker hand probabilities?
Poker card decks always have 52 cards and 2,598,960 possible hand combinations. To work out the probability of a hand, you need to consider the number of ways to achieve it.
For example, there are four different ways to get a royal flush because there are four suits. So, the math to work out the probability of this hand would be: 4 ÷ 2,598,960 = 0.00000154.
Additional Information
A royal flush is the best hand in many variants of poker – ace, king, queen, jack and 10, all of the same suit. This hand cannot be beaten in ace-high games.
A royal flush is a type of straight flush – five suited cards in numerical order. In the event of a tie where more than one player has a straight flush, the highest ranked card at the top of the sequence wins.
As shown in the hand ranking explanations above, traditional poker hands are ranked in the following order:
- Royal flush
- Straight flush
- Four of a kind
- Full house
- Flush
- Straight
- Three of a kind
- Two pair
- One pair
- High card
These traditional hand rankings are used in popular poker formats such as Texas Hold’em and Omaha.
Knowing when to fold is one of the most important skills in poker, especially at the start of a hand. It’s worth considering how your cards rank before the flop – the higher the cards, the stronger they could be.
If you’ve got cards of the same suit you’ll also have an increased likelihood of achieving a flush. If you have closely ranked cards, you could be more likely to form a straight.
After the flop, you might want to think about folding in the following situations: if your pre-flop hand is no longer as strong, if players are betting/raising big and they don’t usually, or if you have a pocket pair but two or more stronger overcards have been dealt.
For more information on poker strategy, including tips and tactics, head here.
Three aces is the highest form of three of a kind. Taking into account that logic, three of a kind will not rank higher than a straight, flush, full house, four of a kind, straight flush or royal flush.
